VNC Security Risks: Why You Need To Secure Your VNC Connections Now!
Is your remote access system a digital open door for cybercriminals? Virtual Network Computing (VNC), a seemingly convenient tool for remote access, harbors significant security vulnerabilities that expose users to a range of digital threats, making it a prime target for malicious actors.
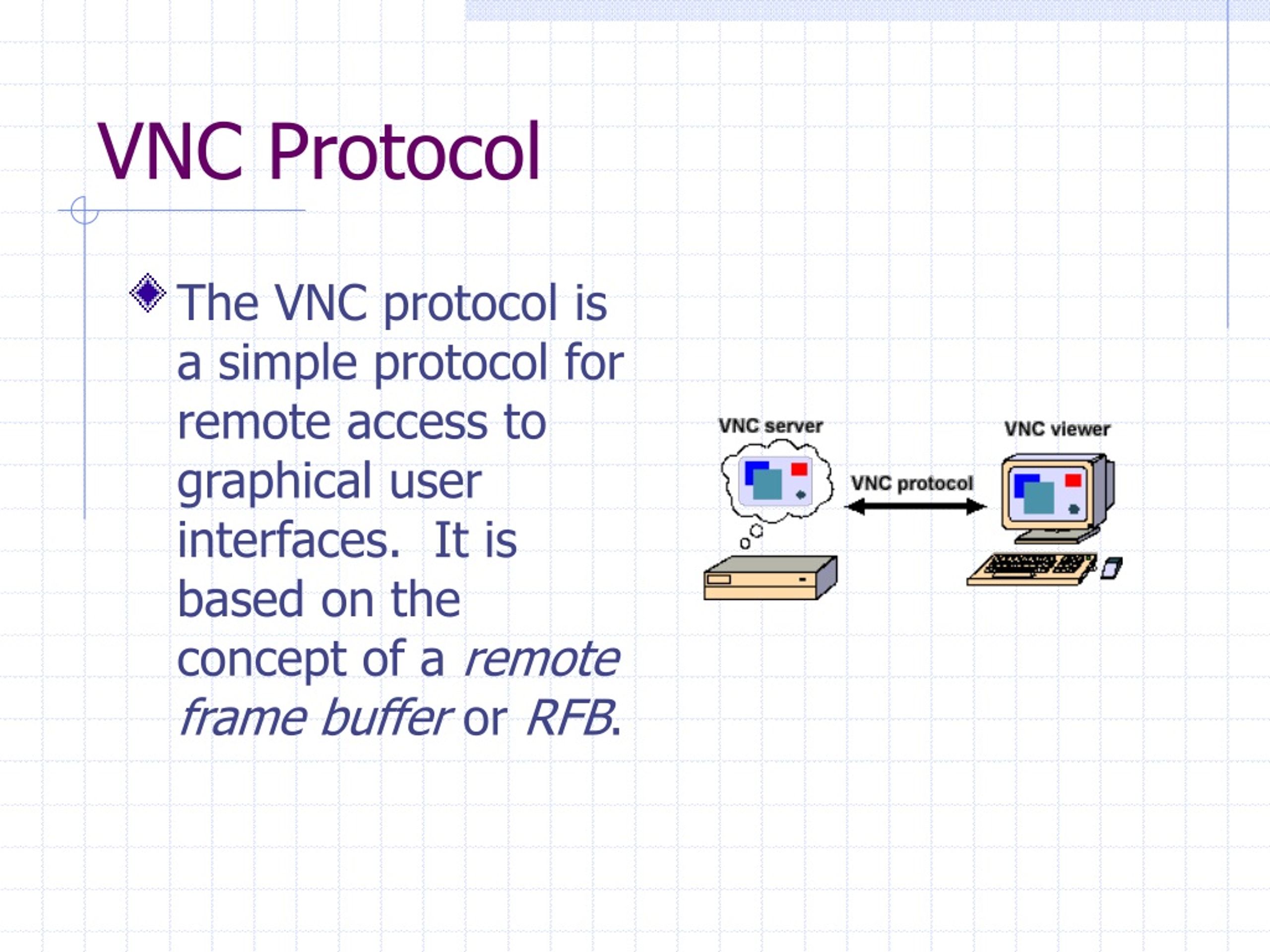
The allure of remote access, the ability to control a computer from a distant location, has made VNC a popular choice. But the convenience comes at a cost. VNC, built upon the Remote Framebuffer (RFB) protocol, is inherently insecure, akin to protocols like Telnet rather than the more secure SSH. While extensions exist to bolster security, the base implementation of VNC remains susceptible. This is a critical point, especially as the digital landscape sees an increasing number of cyberattacks targeting such protocols. Cybercrime is an ever-evolving threat, and understanding the weaknesses within our systems is the first line of defense.
Remote access protocols are fundamental to how we interact with our digital world. Virtual Network Computing (VNC) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) stand out as the two most recognized names in remote access protocols, with Secure Shell (SSH) also finding its use. But, when evaluating the security posture, and the primary question still remains: which of these protocols is the most secure? The answer, unfortunately, is complex, as the security of any protocol relies not only on its inherent design but also on its implementation and configuration. What's clear is that VNC's inherent flaws make it a potentially risky choice.
The core of VNC's security problems lies in its design. Built around the RFB protocol, it transmits screen updates and user input without strong encryption by default. This means that data traveling over the wire can be intercepted and read by anyone with the ability to eavesdrop on the network traffic. This is not an abstract threat; it is a practical risk. Imagine a scenario where sensitive information, such as login credentials or confidential documents, are transmitted unencrypted. Cybercriminals are constantly looking for this type of information to exploit vulnerabilities, and VNC can be a very easy target if the user does not take the proper security precautions.
Adding to the risk is the potential for attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities in VNC implementations. Software bugs or design flaws can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to the remote system, allowing malicious actors to execute commands, install malware, or steal data. This is why it's crucial to keep VNC software updated to the latest version and to be aware of the risks associated with using an outdated protocol.
Another major concern is the increasing prevalence of brute-force attacks against VNC servers. Because of the weak security, attackers will often try to guess passwords and gain access to the system. The lack of robust protection against these attacks makes VNC servers easy targets. This includes the very real threat of being held for ransom via ransomware attacks.
The widespread exposure of VNC instances to the internet is another alarming factor. Dark web intelligence reports, such as those from the firm Cyble, indicate an increase in cyberattacks that target VNC. These cyberattacks are proof that if users do not take the proper measures to protect their systems, hackers can easily exploit them. This heightened level of activity emphasizes the need for vigilance and a proactive approach to securing VNC connections.
This isnt to say that VNC is inherently unusable. With proper configuration and security practices, it can still serve a purpose. But the standard implementation requires users to take very specific measures to avoid the pitfalls. This includes using strong passwords, limiting access to trusted users, and implementing encryption through SSH tunneling or other means. If these steps are not carefully followed, the convenience of VNC will very quickly be overpowered by the risk of a security breach. For many, the effort required to securely configure VNC may outweigh the benefits.
Fortunately, alternatives exist. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) offers built-in security features and is often a better choice for those who require remote access capabilities. Secure Shell (SSH) is another solid option that provides secure access to systems through a command-line interface. Choosing the right protocol depends on the users needs and level of technical expertise. The main point here is to make a conscious choice.
For businesses or individuals who rely on VNC for remote access, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them. Ignoring these vulnerabilities is simply not an option. The digital landscape is constantly shifting, with cybercriminals continuously finding new ways to exploit weaknesses in our systems. This will lead to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Securing VNC connections involves more than just using a strong password. It's about understanding the different layers of security that can be applied and implementing them effectively. Some advice includes using an SSH tunnel, using a strong password, and keeping the software updated.
Here is some advice for securing VNC programs to prevent fraudsters from using vulnerabilities against you.
- Strong Passwords: The first line of defense is a strong password. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information such as dates of birth or names. Use a password manager to generate and store your passwords securely.
- Network Segmentation: If possible, segment your network to isolate VNC servers from the rest of your network. This will limit the damage that can be caused if a VNC server is compromised.
- Regular Audits: Regularly review your VNC configurations and access logs to identify any suspicious activity. Make sure that you are aware of who has access to your VNC servers and what they are doing.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Wherever possible, enable two-factor authentication. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code from an authenticator app, in addition to your password.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Monitor your network traffic for any unusual activity. This can help you to identify and respond to potential attacks before they cause serious damage.
The risks of using VNC are real, and the increasing frequency of attacks targeting these systems shows that the issue needs to be addressed with diligence. By staying informed about security best practices and taking preventative measures, we can significantly reduce our exposure to cyber threats and protect sensitive data.
| VNC Security Vulnerability | Details | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Insecure Protocol | RFB protocol lacks inherent encryption. Data transmitted over the wire can be intercepted and read. | Use SSH tunneling, VPN, or other encryption methods to secure the connection. |
| Vulnerability in Software | Bugs and design flaws in VNC implementations can be exploited by hackers. | Keep software updated, use security patches, and conduct regular security audits. |
| Brute-Force Attacks | Lack of robust protection against brute-force attempts makes VNC servers easy targets. | Implement strong password policies, rate limiting, and account lockout mechanisms. |
| Exposure to the Internet | Thousands of VNC instances are exposed to the internet, increasing the risk of attack. | Use a firewall to restrict access, avoid direct internet exposure, and monitor logs. |
| Unencrypted Sessions | Default VNC sessions often transmit data in plain text. | Always encrypt your VNC sessions with technologies like SSH or VPNs. |
In conclusion, while VNC offers convenience, it should be approached with caution. The inherent security flaws in VNC protocols, coupled with the increasing cyberattacks and the rising threat of ransomware, make it a high-risk option. Whether you are an individual user or a business, it is crucial to fully evaluate and prioritize the security of your remote access system. Choosing a more secure protocol or taking very specific security measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of a security breach.