What Is Remote Iot?
Is the future of connectivity truly in our hands, accessible from anywhere, at any time? The rise of Remote IoT promises precisely that: a world where devices and data, regardless of physical location, are seamlessly integrated and controlled, reshaping industries and redefining possibilities.
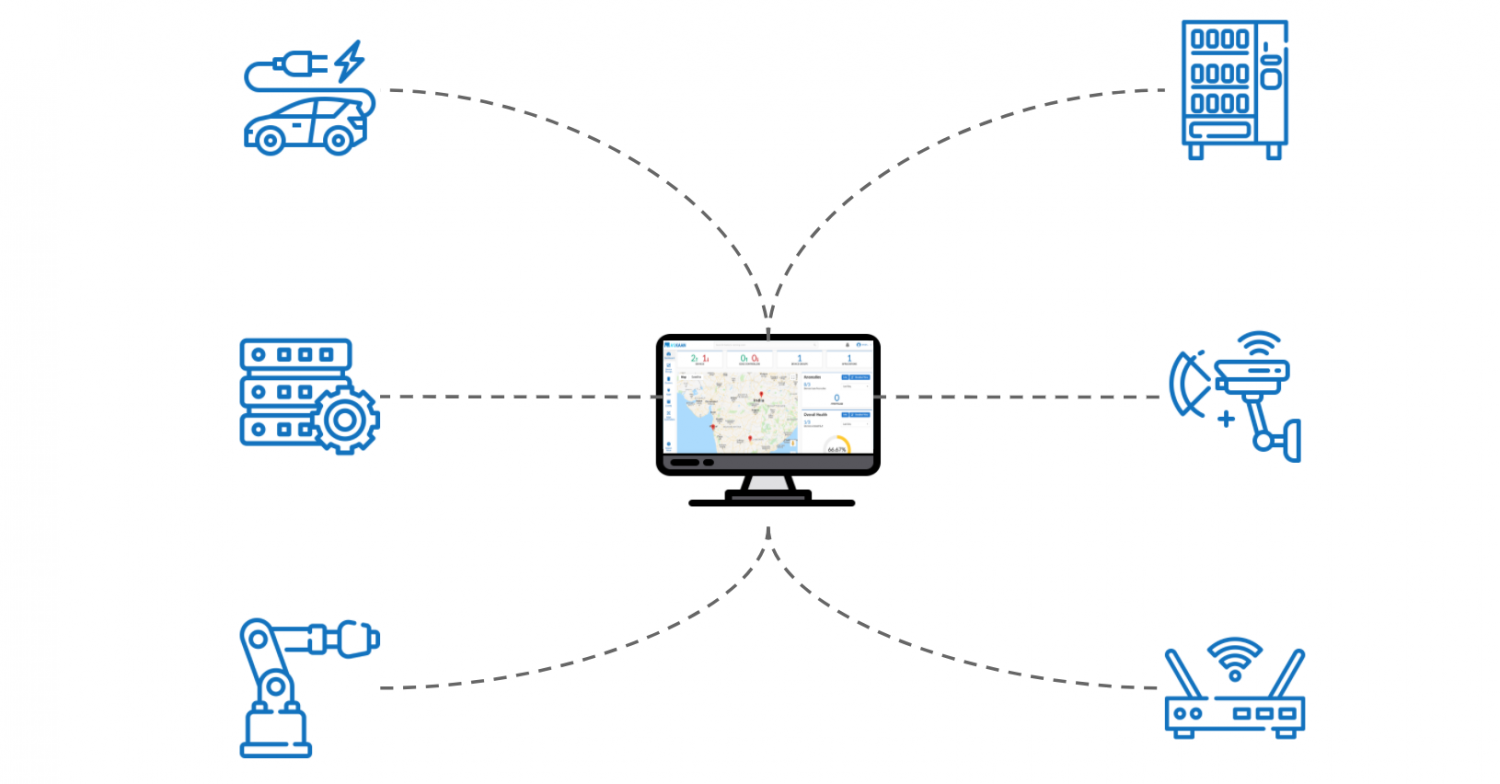
The term "Remote IoT," a convergence of "Remote" and "Internet of Things," encapsulates the ability to manage, monitor, and manipulate devices and systems over long distances. This transcends the limitations of local networks, enabling access to crucial information and control functions from anywhere with an internet connection. It represents a paradigm shift, moving beyond the confines of on-site operations and offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. This evolution is driven by a combination of technological advancements, including increasingly reliable and cost-effective communication technologies, sophisticated data processing capabilities, and the ever-expanding deployment of IoT devices themselves. The potential applications are vast and varied, spanning numerous sectors, from agriculture and healthcare to manufacturing and urban planning. Consider the farmer monitoring soil conditions from a remote office, the doctor remotely assessing a patient's vital signs, or the factory manager controlling machinery across continents. The possibilities are boundless.
Let's delve deeper into the core components and benefits of Remote IoT, exploring its practical applications and addressing the challenges associated with its implementation. This technology harnesses the power of the internet to connect and control a wide array of devices and systems, from simple sensors to complex machinery. The "Remote" aspect is critical, emphasizing the ability to operate and manage these devices from geographically separate locations. Think of it as an extension of the physical world, made accessible and manageable from virtually anywhere. The IoT component refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect and transmit data, forming the foundation for this remote control and monitoring. The integration of these two elements creates a powerful synergy, enabling real-time insights, automated responses, and enhanced efficiency across diverse industries.
The building blocks of Remote IoT are the devices themselves, often equipped with sensors that collect data, such as temperature, pressure, or location. These devices communicate wirelessly with gateways or other network devices, which then transmit the data to a central server or cloud platform. The data is then processed and analyzed, providing valuable insights that can be used to make informed decisions and trigger automated actions. This entire process is typically secured with robust encryption and authentication protocols to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. The communication methods, such as cellular networks, satellite links, or dedicated IoT networks, are carefully selected to ensure reliable and secure data transmission, considering factors like coverage, bandwidth, and cost. The ultimate goal is to provide users with a seamless and intuitive experience, enabling them to monitor and control their devices from any location.
The advantages of embracing Remote IoT are numerous and compelling. Firstly, it dramatically enhances operational efficiency. By monitoring and controlling devices remotely, organizations can reduce the need for on-site personnel, minimize travel costs, and respond to issues more quickly. This leads to faster troubleshooting, reduced downtime, and improved overall productivity. Secondly, Remote IoT facilitates predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from sensors, businesses can anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, preventing costly disruptions and extending the lifespan of their assets. Thirdly, this technology improves resource management. From optimizing energy consumption to monitoring inventory levels, Remote IoT enables organizations to better manage their resources, leading to significant cost savings and environmental benefits. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, Remote IoT empowers data-driven decision-making. The wealth of data collected from connected devices provides valuable insights into operations, enabling organizations to identify trends, optimize processes, and make more informed strategic decisions.
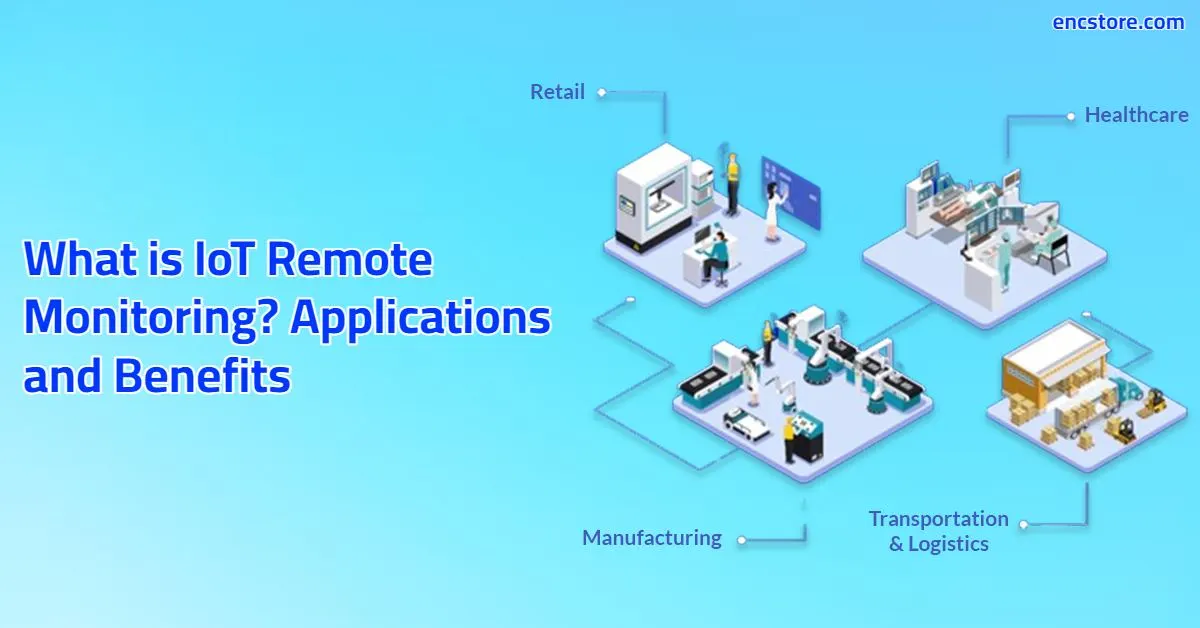
Numerous industries are already benefiting from the transformative potential of Remote IoT. In agriculture, farmers are using Remote IoT to monitor soil conditions, optimize irrigation systems, and track livestock, leading to increased yields and reduced resource consumption. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring systems enable doctors to track vital signs, manage chronic conditions, and provide timely interventions, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. In manufacturing, Remote IoT allows for remote monitoring of machinery, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. In transportation, fleet management systems use Remote IoT to track vehicles, monitor fuel consumption, and optimize routes, improving logistics and reducing costs. In smart cities, Remote IoT is used to manage traffic flow, monitor air quality, and optimize energy consumption, creating more sustainable and livable urban environments.
Despite its immense potential, the implementation of Remote IoT also presents some challenges. Security is paramount. As devices become more connected, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Organizations must implement robust security measures, including encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Another challenge is the integration of diverse systems. The wide variety of devices, communication protocols, and data formats can make it difficult to integrate Remote IoT solutions with existing systems. Interoperability standards and open platforms are crucial to ensure seamless communication and data exchange. Finally, the availability of reliable connectivity is crucial. The effectiveness of Remote IoT depends on a stable and reliable internet connection. Organizations operating in areas with poor network coverage need to consider alternative communication technologies, such as satellite links or dedicated IoT networks.
Considering these challenges, careful planning and execution are essential for successful Remote IoT deployments. Organizations should start by defining their objectives and identifying specific use cases. A thorough assessment of existing infrastructure and the selection of appropriate devices and communication technologies are also critical. They must prioritize security from the outset, implementing robust security measures to protect against cyber threats. Moreover, organizations should establish clear data management policies and practices to ensure data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations. Continuous monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of Remote IoT systems. Investing in skilled personnel and ongoing training is crucial for successful implementation and management. Finally, collaborating with industry experts and leveraging best practices can help organizations navigate the complexities of Remote IoT and maximize its benefits.
Looking ahead, the future of Remote IoT is bright, with continued advancements in technologies, particularly in the areas of 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing, poised to further enhance its capabilities. 5G networks offer significantly increased bandwidth and reduced latency, enabling faster data transmission and real-time control. Artificial intelligence can be used to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and automate decision-making processes. Edge computing allows for processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. These advancements will unlock new opportunities for Remote IoT, including the development of more sophisticated applications and the expansion of its reach into new industries. The convergence of these technologies will pave the way for even more innovative and transformative solutions, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
In conclusion, Remote IoT represents a significant step forward in the evolution of connectivity. It empowers organizations to manage, monitor, and manipulate devices and systems from remote locations, unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. While challenges exist, the benefits are undeniable, and the potential is vast. As technology continues to advance, Remote IoT is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of business, healthcare, agriculture, urban planning, and countless other areas. It is a future where the power of connectivity is truly within our reach, accessible from anywhere, at any time, transforming the way we live and work.