Enhance VNC Security: Best Practices (2024)
Is your remote access setup a potential gateway for cybercriminals? The vulnerability of Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a significant concern, with improperly secured instances readily exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access and control of sensitive systems. Ignoring the potential risks associated with inadequate VNC security is akin to leaving the front door unlocked in a high-crime neighborhood.
The appeal of VNC lies in its simplicity: a straightforward method for accessing a graphical desktop environment remotely. This ease of use, however, often comes at the expense of robust security practices. Many installations are configured with weak or default passwords, unencrypted connections, and lack of multi-factor authentication. These vulnerabilities are well-known and exploited by hackers seeking to infiltrate networks, steal data, and deploy ransomware. Understanding the nuances of securing VNC is no longer optional, but a fundamental necessity for anyone who relies on this technology for remote administration, support, or access.
Let's delve into the critical steps to fortify your VNC deployments, transforming them from potential entry points for attackers into hardened, secure access solutions.
First and foremost, the most basic requirement for security is a strong password. Weak or default passwords are the low-hanging fruit for attackers. Implement strong, unique passwords for all VNC instances. Ensure these passwords meet complexity requirements (minimum length, a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters). Regular password rotation, at least every 90 days, is also a crucial element of a sound security strategy. Furthermore, consider using a password manager to generate, store, and manage these complex passwords. This is especially crucial because weak passwords are the easiest way for anyone to hack into your system.
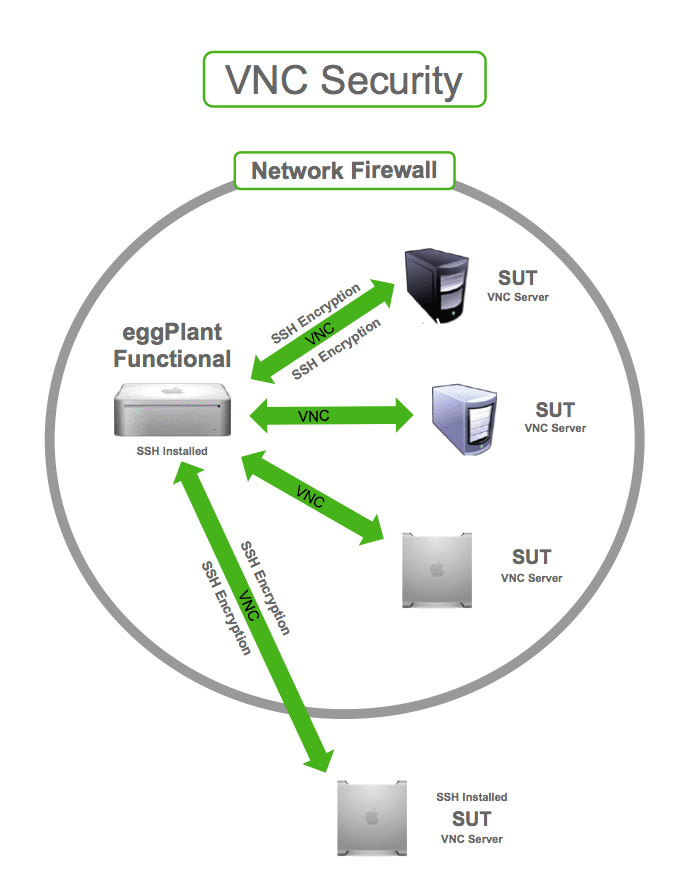
Beyond password strength, encryption is essential for protecting the data transmitted over VNC connections. By default, VNC can transmit data in plain text, meaning that any eavesdropper on the network can potentially intercept and read the sensitive information passing between the client and the server. Utilize encryption protocols, such as SSH tunneling, to create an encrypted connection. SSH (Secure Shell) provides a secure, encrypted channel that wraps VNC traffic, protecting it from prying eyes. SSH tunneling involves forwarding VNC traffic through an SSH connection, which encrypts all data transmitted between the client and server. This method offers a significant upgrade in security compared to unencrypted VNC connections. SSH tunneling can be easily configured on both the client and the server side, providing a practical and effective means of securing your VNC sessions. Also, consider that VPN provides a similar level of encryption but it has more overhead than SSH.
Adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) to VNC access is a powerful defense against compromised credentials. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before granting access. Even if a password is stolen, an attacker will still need a second factor, such as a code generated by a mobile authenticator app or a biometric scan, to successfully log in. There are several methods available for implementing MFA with VNC. One common approach involves integrating VNC with an SSH server that supports MFA, such as Google Authenticator or FreeRADIUS. Other options include using third-party security solutions specifically designed to provide MFA for remote access protocols. The added layer of authentication significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as it requires the attacker to possess more than just stolen credentials.
Another important element is access control. Properly configuring access control lists (ACLs) can restrict access to VNC instances based on IP address or other criteria. Implementing ACLs limits the systems that can connect to your VNC servers, minimizing the attack surface. Only allow connections from trusted IP addresses or ranges. Regularly review and update these ACLs to reflect changes in your network infrastructure and security policies. The more restricted the access, the lower the risk.
Keeping your VNC server software up to date is critical for security. Software vendors regularly release security patches to address vulnerabilities discovered in their products. Applying these updates promptly is essential to protect against known exploits. Regularly check for updates and install them as soon as they are available. Consider implementing automated update mechanisms to streamline the process and ensure that your VNC instances are always protected with the latest security fixes. If possible, the process of updating the VNC servers should be done on the off hours, and always make sure you can have access to the system using physical access or other method to avoid situations.
Consider the use of a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for VNC access. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between the client and the server, protecting the data transmitted over the network. This offers an additional layer of security, especially when accessing VNC servers from public or untrusted networks. Before using a VPN, you may have to look at the VPN configuration, as it will need proper settings to maintain the performance of the system. This is crucial, as sometimes VPN are configured with default settings to make them easy to use, instead of security focused configuration.
Monitoring and logging are crucial for detecting and responding to security incidents. Implement comprehensive logging of VNC activity, including connection attempts, successful logins, and any suspicious activity. Review these logs regularly to identify potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. Set up alerts to notify you of any unusual activity, such as multiple failed login attempts or connections from unexpected IP addresses. The logs can be sent to a centralized logging and analysis server, allowing you to quickly analyze and respond to security threats.
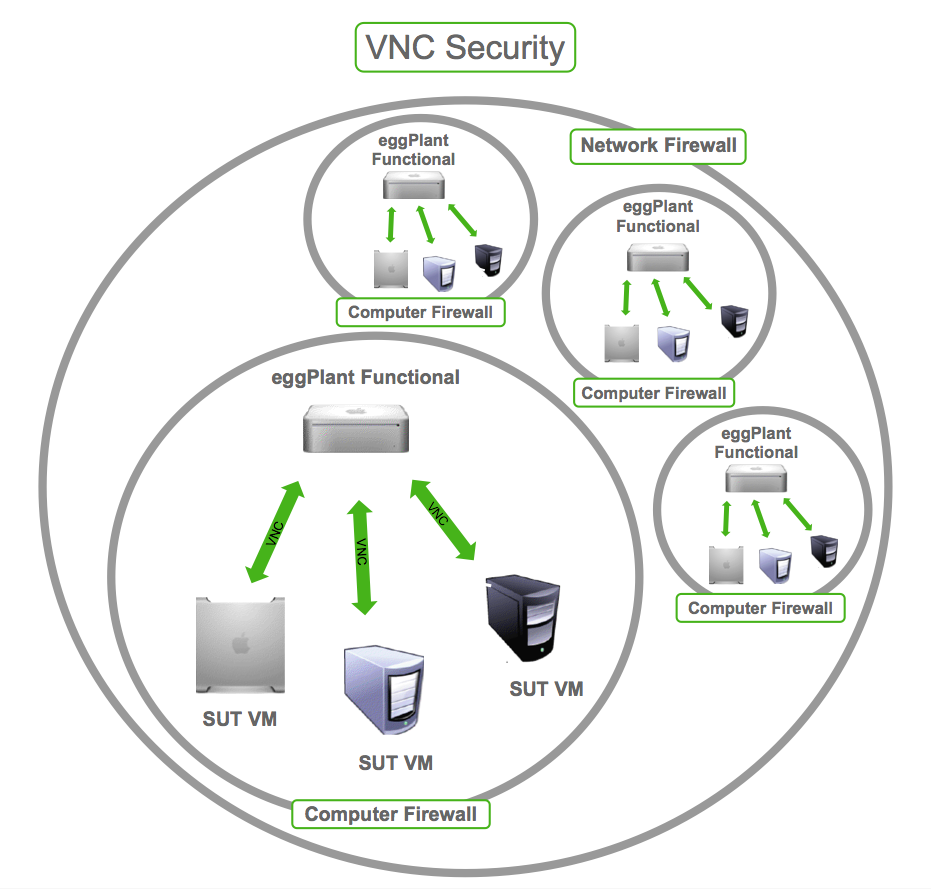
Network segmentation helps to isolate VNC servers from the rest of your network. By placing VNC servers in a separate network segment, you can limit the potential damage if a VNC instance is compromised. Implement firewalls to control traffic flow between network segments, allowing only authorized traffic to pass. This principle of "least privilege" restricts the ability of an attacker to move laterally within your network once they gain access to a compromised VNC instance. A segmentation is also useful to isolate and test your VNC server before putting it on production to ensure the safety of the data.
Restrict VNC Access to Specific Ports. VNC, by default, uses specific ports for communication (typically port 5900 and higher for the actual desktop). You can enhance security by restricting access to these ports on your firewall. Only allow traffic to these ports from trusted IP addresses. This limits the attack surface by preventing unauthorized external connections to your VNC servers. Port restriction can also be combined with other security measures, such as SSH tunneling or VPN, for even greater protection.
The overall security of VNC access relies on a combination of technical measures and good security practices. Regularly review and update your security policies and procedures to adapt to emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify any weaknesses in your VNC configuration and address them promptly. Educate your users about the importance of security and the risks associated with weak or compromised credentials. Implement a robust incident response plan to handle any security breaches quickly and effectively. If you can, use a 3rd party vendor to help with all the process, that can ensure you are implementing everything in a timely and efficiently manner.
By adopting these security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your systems and protect your sensitive data. Remember that security is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. Continuously evaluate and improve your VNC security posture to stay ahead of the ever-evolving threat landscape.