Firewall Iot Devices
Are your smart devices secretly vulnerable? The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has created a sprawling digital landscape, ripe with security vulnerabilities that often go unnoticed, potentially turning your seemingly harmless gadgets into entry points for malicious actors.
The modern home and office are teeming with connected devices: smart TVs, refrigerators, thermostats, security cameras, and countless other gadgets all vying for a spot on your network. Each of these devices, designed for convenience and enhanced functionality, represents a potential security risk. Many IoT devices are manufactured with minimal security features, leaving them susceptible to hacking, malware, and data breaches. The inherent lack of robust security protocols in many of these devices, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, demands a proactive and informed approach to cybersecurity. Simply plugging in a new smart device could inadvertently open the door to a host of threats, jeopardizing not only your personal data but also the integrity of your entire network.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Device Type | Smart TVs, Smart Refrigerators, Smart Thermostats, Security Cameras, Smart Speakers, Smart Lighting, Wearable Devices (Smartwatches, Fitness Trackers) |
| Primary Function | Automation, Entertainment, Monitoring, and Data Collection, remote access and control |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Weak Passwords, Lack of Encryption, Outdated Firmware, Unpatched Software, Default Settings, Known Exploits, Lack of Network Segmentation, Poor Authentication, and Authorization. |
| Common Attack Vectors | Malware Infection, DDoS attacks, Data Theft (Personally Identifiable Information - PII, Health Data, etc.), Remote Control, Device Hijacking (Botnets), Network Intrusion, Surveillance |
| Impact of a Breach | Financial Loss, Identity Theft, Privacy Violations, Disruption of Services, Physical Damage (in some cases), Reputational Damage |
| Recommended Security Measures | Firewalls, Strong Passwords, Regular Firmware Updates, Network Segmentation, Use of a VPN, Two-Factor Authentication (where available), Monitoring Network Traffic, Disabling Unnecessary Features, Educating Users on Phishing and Social Engineering. |
| Additional Considerations | Privacy Policies of Devices, Geo-location services and data collection of the data, physical security access, compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR) |
| Relevant Standards & Protocols | WPA3, TLS/SSL, HTTPS, IoTivity, Zigbee, Z-Wave, MQTT |
| Resource | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) |
The vulnerabilities associated with IoT devices are multi-faceted. One of the primary challenges is the inherent lack of security-focused design in many of these products. Manufacturers often prioritize cost and functionality over robust security features. This can result in devices with weak default passwords, unencrypted communication protocols, and easily exploitable software vulnerabilities. These flaws create attractive targets for cybercriminals, who can leverage them to gain unauthorized access to your network and steal sensitive data. A compromised IoT device can be used to launch attacks against other devices on the network, participate in a botnet, or even be used as a listening device to eavesdrop on conversations.
Further compounding the problem is the rapid proliferation of IoT devices. The market is flooded with new products, and the sheer volume of devices makes it difficult for consumers to keep track of security updates and patches. Many users are unaware of the security risks associated with these devices or lack the technical expertise to properly configure and secure them. This creates a perfect storm for cyberattacks, as attackers can exploit known vulnerabilities in a large number of devices without having to target specific individuals.
Firmware updates, while critical for patching security vulnerabilities, often present their own set of challenges. Many IoT devices are not designed with easy-to-update firmware, making it difficult for users to install the latest patches. In some cases, the manufacturers may not provide timely updates, leaving devices exposed to known threats for extended periods. This lack of timely updates can leave devices vulnerable for long periods, exposing them to a variety of different attacks, including the ability to monitor or extract data.
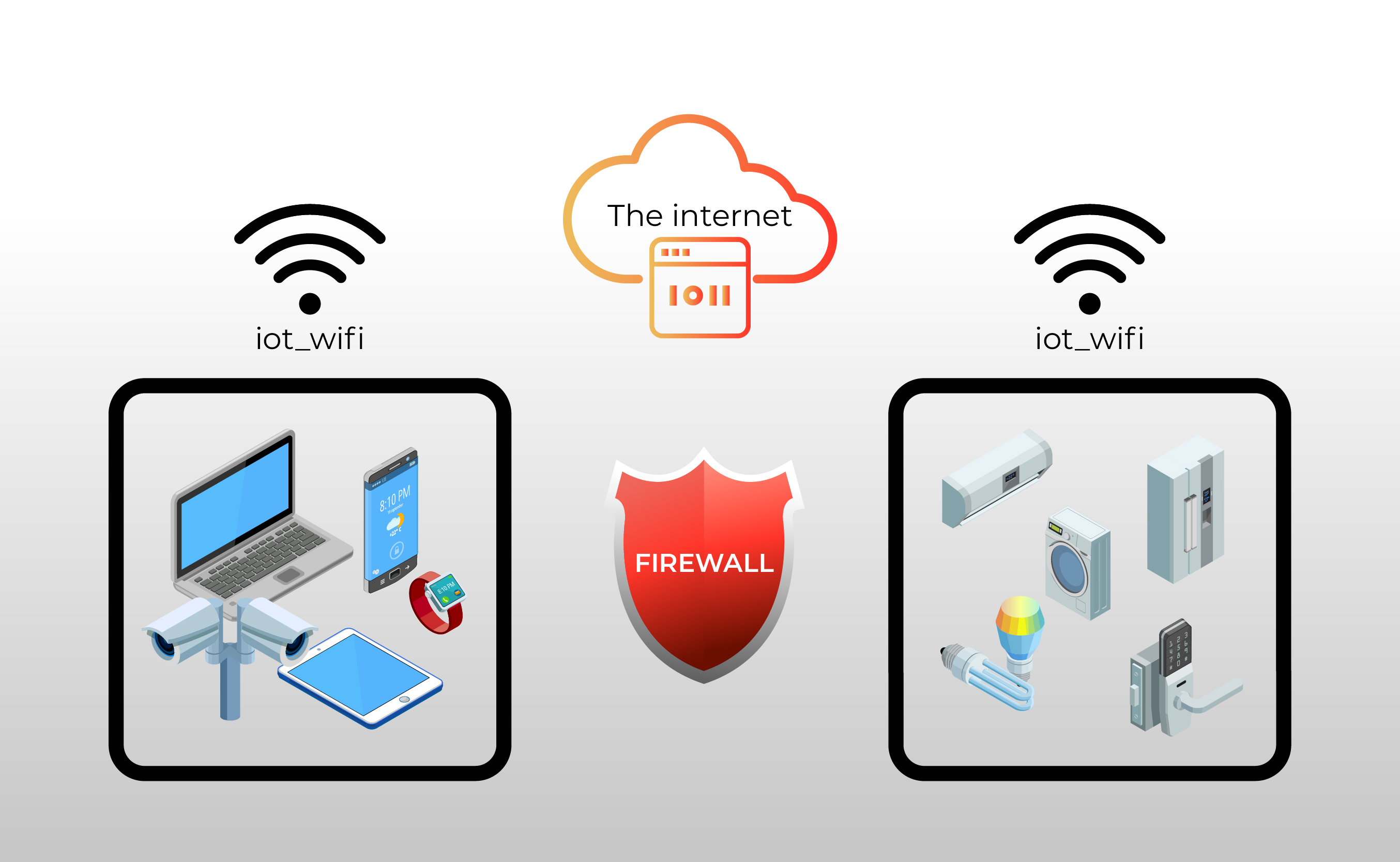
One of the most effective ways to mitigate the risks associated with IoT devices is the implementation of a firewall. A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the outside world, examining incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocking any suspicious activity. A firewall can be configured to filter traffic based on various criteria, such as the source and destination IP addresses, the port numbers, and the type of traffic. This allows you to control the communication between your IoT devices and the internet, limiting their exposure to potential threats. Moreover, the firewall can be set up to monitor traffic in order to identify and block unusual activities, thereby adding an additional layer of protection.
When considering a firewall for your IoT devices, it's important to choose one that is specifically designed to protect against these types of threats. Traditional firewalls may not be sufficient, as they may not be able to effectively identify and block attacks targeting IoT devices. A dedicated IoT firewall should have features such as deep packet inspection, intrusion detection and prevention, and the ability to monitor and analyze the behavior of IoT devices. A robust firewall will also offer regular updates to its threat intelligence database, allowing it to stay ahead of the latest cyber threats. Furthermore, a properly configured firewall should include advanced functionalities, such as the ability to create zones or separate networks that help to isolate the IoT devices from the rest of the network.
Another crucial strategy for enhancing the security of your IoT devices involves network segmentation. Network segmentation involves dividing your network into separate segments or zones, each with its own security policies. This helps to isolate your IoT devices from other devices on your network, limiting the impact of a potential security breach. If an IoT device is compromised, the attacker's access will be restricted to that segment of the network, preventing them from accessing other sensitive data or devices. Network segmentation can be achieved through the use of VLANs (Virtual LANs) or by utilizing a dedicated network for your IoT devices. Each of these segments can then have its own unique security rules and policies.
Besides firewalls and network segmentation, strong password management and regular firmware updates are essential security practices. Always use strong, unique passwords for all your IoT devices and change them regularly. Avoid using default passwords, and be sure to create a strong password that is difficult to guess. Furthermore, you should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone. Regularly check for and install firmware updates from the device manufacturer. Firmware updates often include critical security patches that address known vulnerabilities. By installing these updates, you can ensure that your devices are protected against the latest threats. Be wary of any updates which seem unverified or from an unproven source.
Careful scrutiny of the privacy policies of your IoT devices is a vital aspect of securing your digital life. Before purchasing a new IoT device, take the time to read the privacy policy carefully. Pay close attention to how the device collects, uses, and shares your data. Determine if the device collects personal information, what types of data are collected, and whether the data is shared with third parties. Make sure you're comfortable with the device's privacy practices before connecting it to your network. Be especially cautious of devices that collect sensitive data, such as health information or location data. Understand that giving access to this data, increases your risk.
Education is also a key component of securing your IoT devices. Educate yourself and others in your household about the security risks associated with these devices. Be aware of common attack vectors, such as phishing and social engineering. Be wary of suspicious links or attachments, and never click on links from unknown sources. Teach yourself and others how to identify and report potential security threats. If you are using any devices for business purposes, consult your company's IT security team for any specific guidelines or policies. Regular review of security procedures, especially for high-risk applications or devices, is critical to long-term safety.
In addition to these proactive measures, regularly monitoring your network traffic can help you detect and respond to security threats. Many routers and firewalls provide tools for monitoring network activity. Monitor network traffic for unusual activity, such as unexpected connections or high data usage. If you notice any suspicious activity, investigate it immediately. Use network monitoring tools to identify any unauthorized devices on your network. If you are unable to identify the source of the problem, consider consulting a security professional to analyze your network traffic and identify potential threats. Use the logs generated by your network devices to identify any unusual activity. By proactively monitoring your network, you can detect and respond to potential security threats before they cause significant damage.
The threat landscape surrounding IoT devices is constantly evolving. Staying informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities is essential. Follow security blogs, news websites, and social media channels to stay up-to-date on the latest security news. Subscribe to security alerts from device manufacturers. Stay informed about the latest security best practices. Continuously update your security knowledge. Keep abreast of industry trends and developments. Regularly review your security procedures and update them as needed. Proactive security measures, such as regularly reviewing security procedures, can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach.
As the number of IoT devices in our homes and offices continues to increase, securing these devices is more important than ever. By implementing the security practices described above, you can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach and protect your privacy and data. It is up to each individual to understand the dangers and act appropriately. The combined effort of device manufacturers, consumers, and security professionals is required to ensure a safe and secure IoT ecosystem. This includes developing secure IoT devices, educating users, and responding promptly to emerging threats.